Understanding Identity Management: The Cornerstone of Security
In the rapidly evolving digital world, Identity Management (IdM) has become an essential aspect of organizational security. It refers to policies and technologies that ensure the right individuals access the right resources in an organization at the right times for the right reasons. Identity Management encompasses a range of processes and systems, and it is crucial for protecting sensitive information and complying with regulatory requirements. For more insights, visit Identity Management www.wwpass.com.
The Importance of Identity Management
As organizations move to increasingly digitized platforms, Identity Management has emerged as a vital part of their security infrastructure. The growing number of cyber threats necessitates robust mechanisms to control who can access various systems and data. Here are a few reasons why Identity Management is essential:
- Security: Effective Identity Management systems protect sensitive information from unauthorized access.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many industries face strict regulations regarding data privacy and security, which can be managed through sound identity practices.
- Efficiency: Automating the management of user identities can streamline processes and improve organizational efficiency.
- User Experience: Simplifying user access while maintaining security enhances user satisfaction across the board.
Core Components of Identity Management
Identity Management is not a one-size-fits-all solution. It generally comprises several key components that work together to ensure comprehensive coverage:
1. User Provisioning
User provisioning is the process of creating, managing, and deleting user accounts and permissions. It is crucial for controlling access to information and ensuring users have the appropriate level of access based on their roles.
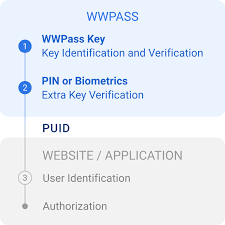
2. Authentication

Authentication verifies that users are who they claim to be. This can involve various methods, from simple passwords to more complex multi-factor authentication (MFA) systems.
3. Authorization
Once a user is authenticated, authorization determines what resources they can access and what actions they can perform. This can be managed through role-based access control (RBAC) or attribute-based access control (ABAC).
4. Identity Governance
Identity governance ensures necessary compliance and security policies through audits, reviews, and reports, allowing organizations to assess their identity management practices continuously.
Challenges in Identity Management
Despite its critical importance, organizations face several challenges in implementing effective Identity Management solutions:
- Complexity: The increasing complexity of IT environments, with a mix of on-premises and cloud-based applications, complicates management.
- Data Privacy Concerns: Striking a balance between securing identities and protecting users’ personal data can be challenging.
- Cost: Implementing comprehensive Identity Management solutions often requires significant investment.
- User Compliance: Users may resist new security protocols, leading to non-compliance and potential security risks.
Modern Solutions for Identity Management
To combat the challenges faced in Identity Management, organizations are increasingly leveraging modern solutions:

1. Cloud Identity Management
Cloud-based Identity Management solutions offer scalability, flexibility, and accessibility, allowing organizations to manage user identities across various environments effectively.
2. Single Sign-On (SSO)
Single Sign-On solutions enable users to authenticate once and gain access to multiple applications, simplifying the user experience while maintaining security.
3. Privileged Access Management (PAM)
PAM solutions provide enhanced security for privileged accounts, which pose higher risks due to their elevated access levels.
4. Identity Analytics
Advanced analytics can enhance decision-making regarding access controls and identify unusual behavior that may indicate a potential security breach.
Conclusion
As organizations navigate the complexities of the digital landscape, effective Identity Management will be paramount. By implementing robust policies and leveraging modern technologies, organizations can protect sensitive data, comply with regulations, and improve operational efficiency. Ultimately, Identity Management not only secures organizational resources but also paves the way for a more cohesive and secure digital experience for users. Embracing these practices will be essential for maintaining a strong security posture in an increasingly hostile cyber environment.
The future of Identity Management will continue to evolve, influenced by technological advancements, user demands, and regulatory changes. Organizations stand to gain significantly by prioritizing Identity Management as a core component of their overall security strategy.
